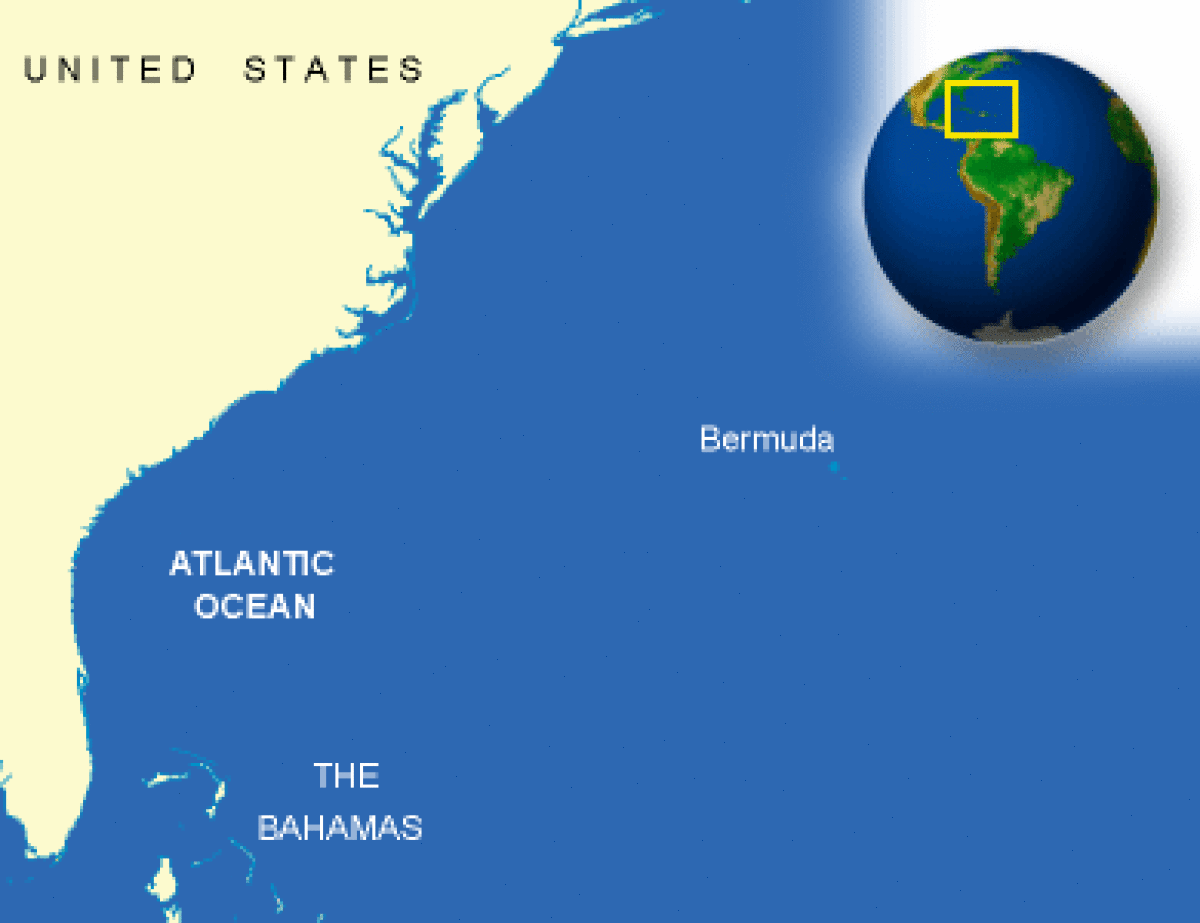
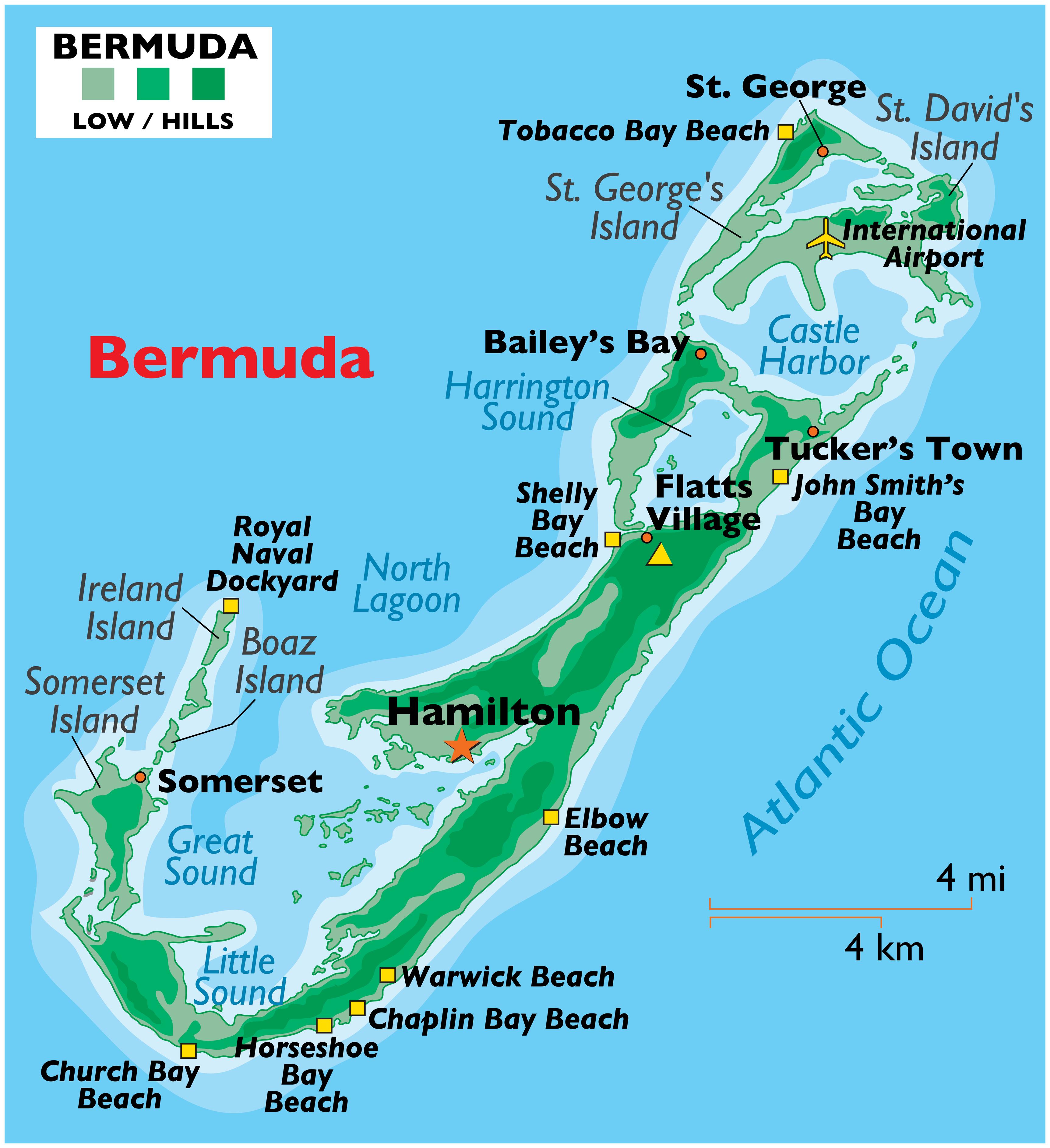
Many travelers and geography enthusiasts wonder whether Bermuda is a country or not. This small yet fascinating archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean often sparks curiosity due to its unique political status. Understanding the true nature of Bermuda's sovereignty requires a deeper dive into its history, governance, and relationship with the United Kingdom.
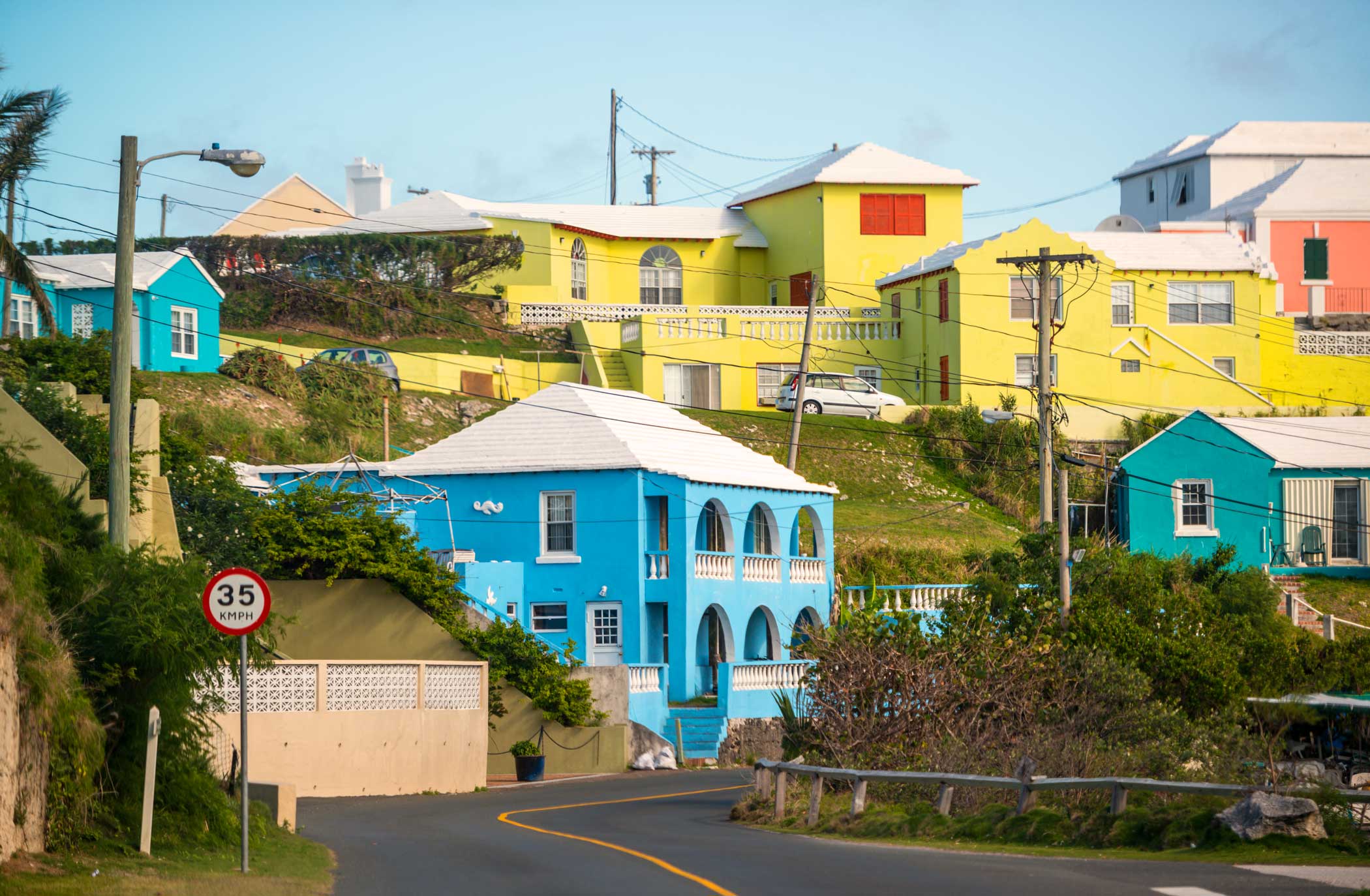
Bermuda has long been a popular destination for tourists, known for its pink-sand beaches, stunning landscapes, and vibrant culture. However, beyond its picturesque beauty lies a complex political structure that sets it apart from independent nations. In this article, we will explore whether Bermuda qualifies as a country and examine its distinct characteristics.
By the end of this discussion, you'll gain a comprehensive understanding of Bermuda's status, its governance system, and its role on the global stage. Let's begin by unraveling the mystery of whether Bermuda is indeed a country or something else entirely.
Read also:Famous Gabrielle The Rise To Stardom And Her Remarkable Journey
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Geography of Bermuda
- Historical Background
- Governance Structure
- Bermuda's Relationship with the UK
- Citizenship and Nationality
- Economic Overview
- Tourism Industry
- International Relations
- Future Prospects
- Conclusion
Geography of Bermuda
Bermuda is a group of islands located in the North Atlantic Ocean, approximately 1,030 kilometers (640 miles) east-southeast of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina. The territory consists of 181 islands, with the main island being simply called Bermuda. Despite its small size, covering only about 53.3 square kilometers (20.6 square miles), it boasts a diverse landscape ranging from sandy beaches to rugged cliffs.
Unique Features of Bermuda
Bermuda's geography offers several unique features that make it stand out:
- Pink sand beaches due to the presence of microscopic organisms called foraminifera.
- A subtropical climate with mild winters and warm summers.
- Rich marine life, making it a popular destination for snorkeling and diving.
According to the CIA World Factbook, Bermuda's highest point is Town Hill, standing at 76 meters (249 feet) above sea level. This geographic diversity contributes significantly to its appeal as a tourist destination.
Historical Background
The history of Bermuda dates back to the early 16th century when it was discovered by Spanish explorer Juan de Bermúdez in 1503. However, it wasn't until 1609 that English settlers arrived after the shipwreck of the Sea Venture, which was en route to Jamestown, Virginia. This event marked the beginning of permanent settlement on the islands.
Key Historical Events
- 1612: The official colonization of Bermuda by the Virginia Company.
- 1684: Bermuda became a British crown colony.
- 1968: Adoption of a new constitution granting greater autonomy to the territory.
Throughout its history, Bermuda has maintained strong ties with the United Kingdom, which continue to shape its current political status.
Governance Structure
Bermuda operates as a parliamentary dependency under the British crown. It has its own constitution and a bicameral parliament consisting of the Senate and the House of Assembly. The Governor, appointed by the UK monarch, serves as the head of state, while the Premier acts as the head of government.
Read also:Taliacutea Acapulco Shore The Rising Star Of Mexican Reality Tv
This governance structure allows Bermuda significant autonomy in domestic affairs while relying on the UK for defense and foreign relations. The legal system is based on English common law, ensuring stability and consistency in governance.
Bermuda's Relationship with the UK
Bermuda's relationship with the United Kingdom is defined by its status as a British Overseas Territory (BOT). This arrangement provides Bermuda with protection and support in areas such as defense, security, and diplomacy. In exchange, Bermuda contributes to the UK's global influence and strategic interests.
Benefits of the Relationship
- Access to UK citizenship for Bermudians.
- Financial assistance during economic challenges.
- Representation in international forums through the UK.
Despite this dependency, Bermuda retains considerable control over its internal matters, making it a unique example of a self-governing territory within the British Commonwealth.
Citizenship and Nationality
People born in Bermuda are British Overseas Territories citizens (BOTC). However, most Bermudians also hold full British citizenship, allowing them to travel and reside in the UK without restrictions. This dual citizenship status reflects Bermuda's close ties with the United Kingdom.
The Bermuda Immigration Act regulates immigration and naturalization, prioritizing skilled workers and investors. This policy aims to maintain the territory's economic stability while preserving its cultural identity.
Economic Overview
Bermuda boasts one of the highest GDP per capita in the world, driven primarily by its financial services sector and tourism industry. The territory is a leading center for offshore insurance and reinsurance, attracting major international companies. Additionally, its strategic location makes it an important hub for shipping and commerce.
Key Economic Sectors
- Financial services: Accounting for over 60% of GDP.
- Tourism: Generating significant revenue through visitor spending.
- Real estate: A booming industry due to limited land availability.
Data from the Bermuda Department of Statistics shows that the territory's economy remains robust, with a focus on innovation and sustainability.
Tourism Industry
Tourism plays a vital role in Bermuda's economy, attracting millions of visitors annually. The islands' natural beauty, rich history, and vibrant culture create an ideal destination for travelers seeking relaxation and adventure. Key attractions include:
- Horseshoe Bay Beach: Famous for its pink sand and clear waters.
- Bermuda Aquarium, Museum & Zoo: Offering educational exhibits and wildlife encounters.
- Historic St. George's: A UNESCO World Heritage Site showcasing colonial architecture.
According to the World Travel & Tourism Council, tourism contributes approximately 15% to Bermuda's GDP, underscoring its importance to the local economy.
International Relations
As a British Overseas Territory, Bermuda does not have independent representation in international organizations. However, it participates in regional forums such as the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS) through the UK. This involvement allows Bermuda to engage with global issues and promote its interests on the international stage.
Furthermore, Bermuda maintains strong diplomatic relations with countries around the world, fostering cooperation in areas such as trade, security, and environmental conservation.
Future Prospects
The future of Bermuda as a territory holds both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, its strategic location and well-developed infrastructure position it favorably for continued growth in key industries. On the other hand, global economic trends and geopolitical shifts may impact its relationship with the UK and other partners.
Efforts to diversify the economy, invest in renewable energy, and promote sustainable tourism could enhance Bermuda's resilience and competitiveness in the years to come. The territory's ability to adapt and innovate will be crucial in navigating these changes.
Conclusion
After exploring Bermuda's geography, history, governance, and economy, it becomes clear that Bermuda is not a country in the traditional sense. Instead, it is a British Overseas Territory with significant autonomy in domestic matters. This unique status allows Bermuda to benefit from the UK's protection and support while maintaining its distinct identity and culture.
We invite you to share your thoughts on this article and explore other fascinating topics related to geography and politics. Feel free to leave a comment below or check out our other articles for more insights. Together, let's continue learning and expanding our understanding of the world around us!